Signs and Symptoms of Different Thyroid Diseases
Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in your neck. It is an endocrine gland that makes hormones. Hormones secreted by your thyroid control the rate of various activities in your body. These include how fast your heart beats and the speed that you burn calories. How all activities work together is known as the body’s metabolism.
***According to Medlineplus.gov (2022), approximately 15 million Americans live with an undiagnosed thyroid condition.***
We Can Help!
Here at Senior Healthcare Advisors, we specialize in maximizing Medicare benefits! We are here to guide you in understanding and enrolling in the Medicare benefits you are entitled to and qualify for. Give us a call today.
888.809.2440
What Does My Thyroid Do?
- Regulates your body temperature.
- Controls your heart rate.
- Controls your metabolism, which is responsible for transforming the food you eat into energy that helps your body function.
Thyroid Conditions Include
- Hyperthyroidism – when your thyroid gland makes more thyroid hormones than your body needs
- Hypothyroidism – when your thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormones
- Goiter – enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Thyroiditis – swelling of the thyroid
- Thyroid nodules – lumps in the thyroid gland
- Thyroid cancer
Doctors diagnose thyroid diseases by conducting a physical exam, examining your medical history, and taking blood tests specific to your thyroid. Thyroid surgery, medications, or radiation treatments are necessary in some cases. Sometimes, a biopsy is conducted to test for cancer.
CLICK HERE: https://seniorhealthcareadv.com/
Thyroid Self-Examination
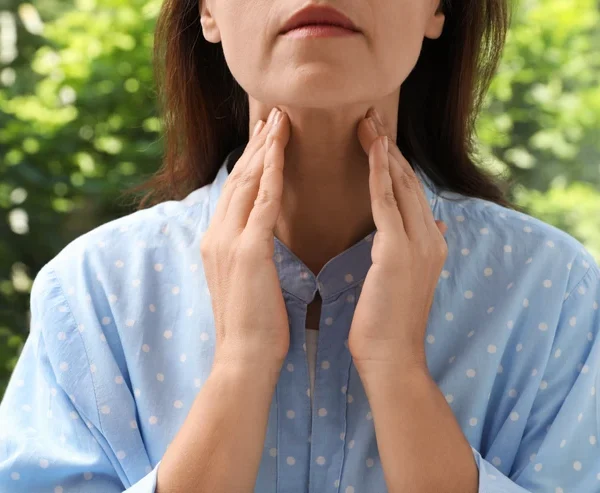
By conducting an easy neck self-exam, you can detect early signs of thyroid disease. Enlargements or lumps in your neck may be indicative of a thyroid condition. Follow this step-by-step thyroid self-exam guide:
What you’ll need: A glass of water and a handheld mirror
Step-by-Step Guide for Thyroid Self-Exam Neck Check
- While holding the mirror in your hand, focus on the front (just below your Adam’s apple) area of your neck. That is where your thyroid is located.
- While focusing on your neck area in the mirror, tilt your head back.
- With your head tilted back, take a medium-sized sip of water and swallow.
- Look at the same area of your neck as you swallow, and check for any protrusions or bulges when you are swallowing.
- **Important** Don’t confuse your thyroid gland with your Adam’s apple. Your thyroid is lower in your neck than your Adam’s apple, closer to your collarbone.
- Repeat the process several times.
- If you notice any protrusions or bulges in this area, consult your physician. You may have a thyroid nodule or enlarged thyroid gland.
HYPOTHYROIDISM
Hypothyroidism is when your thyroid is underactive. If you have Hypothyroidism, your body is not producing enough thyroid hormones, leading to several health conditions, such as heart disease, obesity, and joint pain.
There are various signs and symptoms of Hypothyroidism, depending on how severe the hormone deficiency is. At first, the symptoms may barely be noticeable, but you might start noticing weight gain and fatigue. You may, in the beginning, just think you are experiencing the natural aging process, but as the condition continues to slow down your metabolism, the symptoms will become more obvious. Complications tend to develop over a period of years slowly.
Hypothyroidism Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Dry skin
- Increased sensitivity to cold
- Constipation
- Puffiness in the face
- Weight gain
- Muscle fatigue
- Elevated cholesterol
- Hoarseness
- Muscle stiffness, aches, and tenderness
- Swelling, stiffness, or pain in your joints
- Depression
- Thinning hair
- Slowed heart rate
- Memory problems
- Goiter (enlarged thyroid gland)
Hypothyroidism Causes
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease commonly causing Hypothyroidism. It causes your immune system to produce antibodies that attack your own thyroid cells, making it difficult for your thyroid gland to produce sufficient hormones.
- Hyperthyroidism treatments sometimes go to the extent of causing Hypothyroidism, creating the need for life-long thyroid medication treatment.
- Thyroid surgery. Removal of your thyroid gland’s entire or large portion diminishes its ability to produce sufficient hormones, causing a life-long medication regime.
- Radiation therapy is used to treat thyroid cancer, leading to Hypothyroidism.
- Medications such as lithium can cause Hypothyroidism. Talk to your doctor about all of your medications if you are experiencing hypothyroidism symptoms.
Call Senior Healthcare Advisors at 888.809.2440 | TTY 711
HYPERTHYROIDISM
An overactive thyroid is known as hyperthyroidism. When you have hyperthyroidism, it means your thyroid gland is producing more thyroid [triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)] hormones than your body needs. It can increase your body’s metabolism.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism (Note: Seniors may not experience any symptoms)
- Unexpected weight loss
- Muscle weakness
- Irregular or rapid heartbeat
- Increase anxiety
- Insomnia
- Goiter: Swelling of the neck from an enlarged thyroid gland.
- Hair loss
- Thyroid Eye Disease: Bulging of the eyes
- Muscle weakness.
- Increased appetite
- Irritability
- Sweating
- Diarrhea
- Vision changes
- Warm, thin, and moist skin
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Graves’ disease is an immune system disorder that affects your thyroid. This condition makes your thyroid overproduce thyroid hormone. It is hereditary and accounts for 85% of hyperthyroidism cases in the U.S. It is more common in females.
Thyroiditis is a condition where your thyroid becomes inflamed. It can occur within a year after having a baby, known as postpartum thyroiditis, and lead to Hypothyroidism.
A thyroid nodule is a lump in your thyroid gland that stimulates more thyroid hormones than your body needs. However, they are rarely malignant or cancerous.
Consuming too much iodine. Excess iodine from medications or your diet increases hormones production, leading to hyperthyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism Treatments
- Antithyroid drugs block the ability of your thyroid to produce hormones. They work to control your thyroid rapidly.
- Radioactive iodine: is a medication is taken by mouth that is absorbed by your overactive thyroid cells. The radioactive iodine causes cell damage, which shrinks your thyroid and lowers your thyroid hormone levels. Most individuals who undergo this treatment have to stay on life-long thyroid medication.
- Surgery: Your doctor may conduct a thyroidectomy (removing your thyroid gland). That will automatically cure your hyperthyroidism, but it will also leave you with Hypothyroidism, requiring you to take thyroid medications (life-long) to keep normal thyroid levels.
- Beta-blockers: Beta-blockers block the thyroid hormone’s activities in the body. They do not affect your thyroid levels, but they treat the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as shakiness, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety.
Untreated Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism can affect various parts of your body, ranging from your bones (skeletal system) and your heart (vascular system).
If left untreated, complications include
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Stroke.
- Congestive heart failure.
- Osteoporosis.
**If you are experiencing hyperthyroidism symptoms, you must see your physician make a proper diagnosis, and treatment is prescribed.